If you have a few minutes to spare, measure your waist to know how healthy you are. Stand straight and exhale before measuring your waist 1-2 inches above your hip bones. If you are male and waist measurements are over 40 inches or a female with waist over 35 inches[1], you are facing a potentially dangerous amount of belly fat[2].
Whether you have a slight beer belly or a muffin top, belly fat can pose a severe risk to your health[3]. Even if you are not obese and have a healthy lifestyle, excess fat in your abdomen must be checked. Read on to know why belly fat can be problematic, how non-surgical fat removal methods can help, its benefits and costs.
Average Cost of Surgical Fat Removal Methods in India
| Treatment Type | Cost Range in India | Brief Details |
|---|---|---|
| Liposuction | Rs. 80,000 – Rs. 2,00,000 | Remove stubborn fat deposits |
| Abdominoplasty (Tummy Tuck) | Rs. 80,000 – Rs. 1,50,000 | Eliminate belly fat, tighten muscles |
Lets have the look at the different methods in details with prices –
Liposuction
This cosmetic procedure is performed to surgically remove the stubborn fat deposits in your abdomen to flaunt a toned and sculpted look. The cost of liposuction surgery in India starts from Rs. 80,000 and can go up to Rs. 2,00,000 based on the extent of fat removal in the targeted site.
Abdominoplasty
It is known as a tummy tuck. This surgical removal procedure eliminates excess fat in the belly region and tucks the loose muscles to create a smooth and firm abdomen. The cost of a tummy tuck or abdominoplasty procedure in India ranges between Rs. 80,000 to Rs. 1,50,000. The average price of a tummy tuck procedure comes to about Rs. 1,15,000.
Cost of Non-Surgical Belly Fat Removal Methods
| Treatment Type | Cost Range in India (Per Session) | Brief Details |
|---|---|---|
| Cryolipolysis | Rs. 15,000 – Rs. 45,000 | Fat freezing technique |
| High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) | Rs. 20,000 – Rs. 100,000 | Skin tightening, fat reduction |
| Radiofrequency Treatments | Rs. 3,000 – Rs. 10,000 | Skin tightening, wrinkle reduction |
| Laser-Assisted Fat Removal | Rs. 50,000 – Rs. 200,000 | Lipolysis with laser aid |
What is Belly Fat?
Belly fat refers to the buildup of fat across your abdomen area. Belly fat is of two types based on its location in your abdomen. They are:
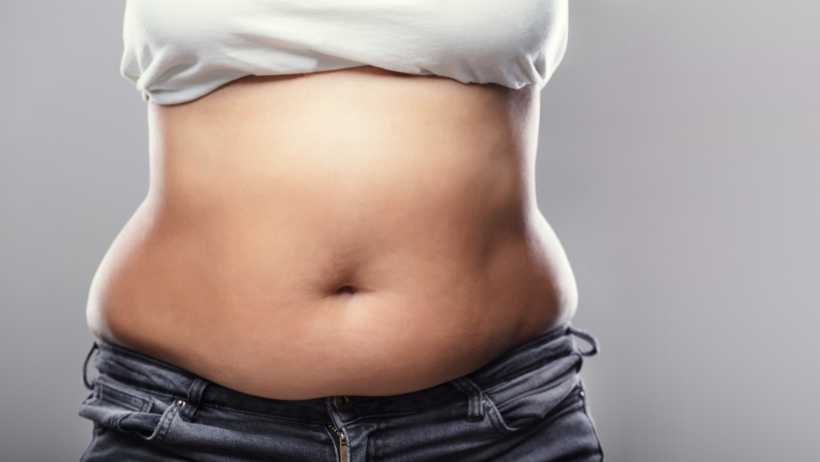
Subcutaneous belly fat
Also called SAT or Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue, this type of belly fat lies under your abdominal skin[5]. The jiggle you feel in your belly when moving indicates the presence of soft subcutaneous fat in the abdomen. Generally, women are found to have a high amount of this belly fat type when compared to their male counterparts[6]. This type of fat doesn’t have a strong link in risk of getting chronic diseases. But, if you have too much body fat, including SAT, you might create certain types of cancers, heart issues, and type 2 diabetes as you age[7].
Visceral belly fat

It is also referred to as VAT or Visceral adipose tissue and lies much deeper in your abdomen[8]. It is called harmful belly fat, which surrounds your internal organs like the pancreas, liver, and kidneys. This type of fat is metabolically active and has more nerves and blood cells than SAT. The visceral fat might hinder your blood sugar levels by increasing your body’s resistance to insulin[9], leading to type 2 diabetes development[10]. It also causes body inflammation, which can make your body prone to various diseases[11].
Reasons Behind Accumulation of Belly Fat
Factors like the foods you consume, hormones, and a sedentary lifestyle might contribute to abdominal fat buildup. Below are the top contributing factors that are culprits causing fat accumulation in your abdomen.
1. Drinks and Foods High in Sugar
Consuming foods loaded with added sugar like baked goods, pastries, packaged foods, sweetened cereals, protein bars, flavoured yoghurts, juices, and colas[12] leads to increased visceral fat in your belly[13].
2. Alcohol Intake
High levels of alcohol intake can be harmful to your health[14], as it will cause obesity, cancer, liver issues, and inflammation[15]. The CDC or Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends you abstain from alcohol or have two drinks a day for males and women. It’s one drink per day[16]. Consuming excess amounts of alcohol will cause the accumulation of visceral fat[17] and lead to a high BMI or Body Mass Index[18].
3. Sedentary Lifestyle
Following an inactive lifestyle can hurt your overall health[19]. If you are physically inactive and follow a sedentary lifestyle, it will have a direct impact on your subcutaneous and visceral fat in the abdomen[20]. A study showed that people who sat for more than 8 hours per day, excluding their bedtime, faced a 62% risk of developing obesity than the ones who sat for 4 hours[21].
4. Low Protein Intake
Diets rich in protein prevent weight gain, repair muscle, help in metabolism, and burn more calories to maintain the ideal body weight[22]. Several studies[23] show that people who follow a proper diet with high protein will not develop excess belly fat[24].
5. Menopause Stage
Accumulation of belly fat among women going through menopause is common[25]. During menopause, the estrogen levels in your body lower drastically[26], which can lead to the accumulation of abdomen fat than other parts[27].
6. Imbalance in Gut Bacteria
As already discussed, bad eating habits such as foods low in fibre and high in sugar can cause the growth of unhealthy bacteria in your gut[28]. An unhealthy imbalance of gut bacteria[29] will cause the accumulation of belly fat and increase weight gain. Especially, having a higher number of Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes bacteria is responsible for higher visceral fat deposition[30].
7. Stress Hormone
Your body recovers from psychological or physical stress when the adrenal glands release a stress hormone called cortisol to survive it[31]. However, if you are under chronic stress, your body produces excess cortisol levels, which causes visceral fat accumulation. This also occurs when people try to binge eat calorie-rich foods to seek comfort from their stress, which also leads to obesity and belly fat[32]. Sometimes, chronic stress works in your body negatively, where excess belly fat will hike your cortisol levels[33].
Health Implications of Belly Fat
Having an excess amount of abdominal fat is harmful to the health and can increases the risk of developing chronic conditions. Even though the presence of visceral fat is around 20% of the overall body fat, it is strongly associated with the development of chronic diseases[34]. Visceral fat is also called to as active fat. It is responsible for the production of hormones and inflammatory proteins, which affect your blood pressure levels, fat in the blood, insulin resistance, and systemic inflammation[35]. The accumulation of visceral fat across your abdominal organs can lead to the development of chronic conditions like dementia[4], heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
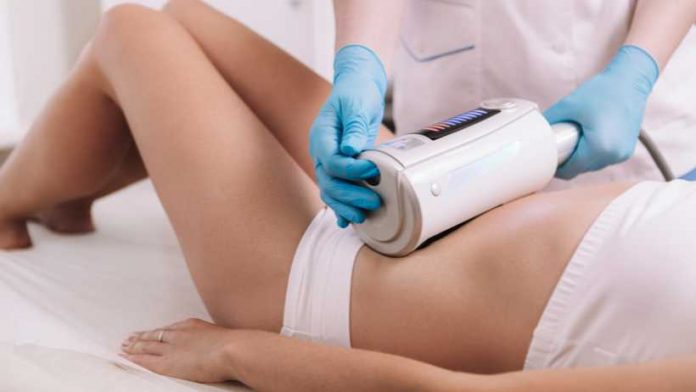
Non-Surgical Belly Fat Removal Methods
—
Non-surgical fat removal procedures[36] have become very popular in recent times, as several people are on the lookout for ways to lower their belly fat without going under the knife. Non-surgical procedures are proven to be effective for belly removal and are considered safe alternatives for surgical procedures[37]. Choose the proper non-surgical belly fat removal technique to achieve your health goals quickly.
1. Cryolipolysis or Coolsculpting
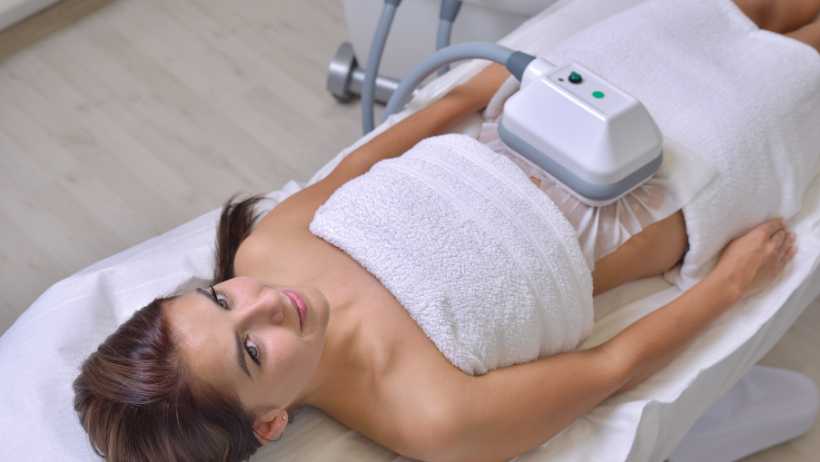
Cryolipolysis or Coolsculpting method is also referred to as fat freezing treatment. It is considered one of the effective techniques for the reduction of belly fat[38]. It is based on non-invasive technology to cool and break down fat cells, lowering stubborn fat pockets. Your skin surgeon would place a cupped or paneled device over the upper skin surface of the treatment area. It then brings down the temperature of the targeted site for freezing the fat cells before destroying them. It is a safe procedure that uses very low temperatures to freeze down the fat deposits. It is beneficial because:
- It is an FDA-approved treatment[39] to remove stubborn fat in your abdomen, hips, buttocks, chin, thighs, and underarms.
- It is perfect for those looking for a minimally invasive procedure to cut down fat bulges without overall body reshaping.
- Each session lasts 30 to 60 minutes, and the results are visible within a few weeks.
- You may experience a little discomfort when undergoing this treatment. But you can do your favourite activities during the sessions, like reading a book, listening to music, or any other activity you love.
- The results of Cryolipolysis or Coolsculpting are long-lasting, as you will not gain excess body weight even after the treatment is complete.
2. High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound
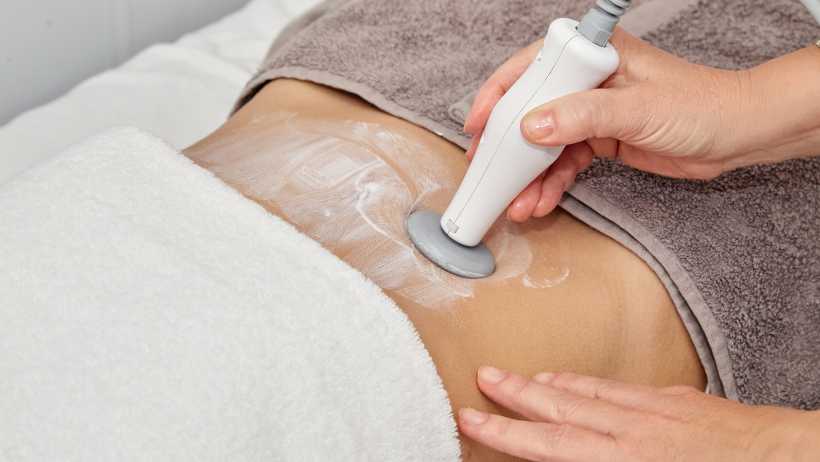
This fat reduction procedure utilizes high-intensity ultrasound waves to heat the fat cells in the targeted region. The ultrasound energy penetrates the deep skin layers in your abdomen to break down fat cells and stimulate collagen renewal[40]. It utilizes high-intensity focused ultrasound technology to distribute the heat energy uniformly, maintaining a constant temperature. It is an effective treatment because:
- This session utilizes FDA-approved medical devices for fat removal.
- It doesn’t require downtime after treatment; you can return to your job as usual.
- It produces a mild heat and tingling sensation and causes minimal discomfort.
- The positive results will be noticeable in 4 weeks, as it will tighten, contour, and lift the abdomen.
3. Radiofrequency Treatments
This treatment involving radiofrequency is performed to remove excess fat in the abdomen and other parts of the body[41]. It uses controlled heat application on the fat cells accumulated in your belly and breaks them down without causing any damage to the skin or muscle surrounding it. It not only lowers fat but also kindles collagen production for firming the loose skin in the abdomen caused by fat loss[42]. It is an excellent choice as:
- It is cleared by the FDA for its safety and effectiveness.
- This non-invasive treatment simultaneously produces warm and cool sensations to keep you comfortable throughout the sessions.
- The results of this treatment will be visible after a couple of sessions and require no downtime.
- You may have some discomfort, bruising, or swelling, which will fade away after a few hours.
4. Laser-Assisted Fat Removal
This treatment is perfect for achieving a well-contoured abdomen. It works by applying controlled laser heat to dismantle the accumulated subcutaneous fat in your belly area. During this laser procedure, the fat tissue in the targeted area gets heated until it breaks down. However, the procedure also utilizes a cooling mechanism to prevent your skin from damage. It is an ideal treatment for belly fat removal, as:
- This is FDA-approved for lowering abdomen fat to cut down the fat tissues in the body.
- This procedure is painless and may give a warm sensation, which will not produce any discomfort.
- Each session may last around 30 minutes, and the results will be noticeable from the 6th week.
- Assures long-term results, as you don’t put on weight after the procedure.
Factors affecting the cost of Non-Surgical Belly Fat Removal
- It depends on how much belly fat you need to get rid of to have a toned body.
- The number of belly fat reduction sessions you will require will affect the cost of the belly fat removal procedure.
- The geographic location of your clinic, such as renowned cities in the country like Hyderabad or Chennai, will influence the treatment cost.
- Using advanced technologies for belly fat reduction will affect the cost of abdomen fat reduction techniques.
- Choose a skin and beauty clinic with a reputation for having a high success rate in offering non-surgical procedures for belly fat removal. It will affect the overall treatment costs.
Benefits of Non-Surgical Belly Fat Removal
Non-surgical fat removal procedures are very effective and safe for slimming down without an invasive procedure. Here are a few reasons why they can be beneficial.
- Completely Non-invasive: Non-surgical fat removal procedures don’t involve making any incisions, needle shots, or other cuts like surgical procedures. All it needs is just a few sessions of short periods, which an expert dermatologist will perform.
- Quick Results: Unlike liposuction procedures, these non-surgical options provide visible results quickly. Soon after the initial session, you will see a significant improvement in your abdomen size and shape.
- Zero or Less Discomfort: These non-surgical procedures are mostly painless and don’t cause any serious discomfort.
- Not Very Expensive: Reducing belly fat through non-surgical options is much more affordable when compared to their surgical counterparts. Consider non-surgical options if you wish to flaunt a toned belly within a budget.
- Extremely Safe: You need not have concerns before opting for non-surgical procedures for belly fat removal, as they are completely safe. These procedures utilize FDA-approved technology and devices, which makes it a safe choice.
Who is a Good Candidate for Non-Surgical Belly Fat Removal?
- Individuals struggling to reduce unwanted and stubborn fat can make their belly look unsightly.
- People who don’t have enough time for diets and weight loss training programs due to their busy work schedules.
- Individuals who prefer to have firm, tight, and young-looking skin in their abdomen area.
- People who are 10 Kg more than their ideal body weight can avail of these non-surgical treatments.
- Individuals committed to maintaining a healthy lifestyle to maintain lasting results are offered belly fat reduction methods.
- People who don’t have any skin infections, are non-pregnant women, don’t use any pacemaker devices, or have any chronic medical conditions are eligible for these treatments.
Parting Thoughts
Having a healthy lifestyle and a well-toned body without any unsightly fat pockets bulging through your dress is a dream of many people. To
dispose of stubborn belly fat, you might want to go for non-surgical belly fat removal methods to look beautiful and feel confident. To get the most out of these treatments, it is essential to choose the services of a renowned weight loss clinic like Kolors Healthcare near you to get safe and visible results quickly. Please book an appointment today for an initial consultation with their weight loss experts to get assessed and advice on which method will work best for you. Contact Kolors Healthcare for more information on various non-surgical belly fat removal methods.
References
- Centre for Cancer Epidemiology, Tata Memorial Centre, Mumbai, 400 012, India – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27573429/
- European Journal of Preventive Cardiology – http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/2047487313492631
- Ian J Neeland, Aslan T Turer, Colby R Ayers, Jarett D Berry – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25975481/
- Kaiser Permanente Division of Research, 2000 Broadway, Oakland, CA 94612, USA – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18367704/
- Department of Biotechnology, Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar University, Vidyapath, Lucknow 226 025, Uttar Pradesh, India – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6702693/
- Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, College of Pharmacy, Marshall B. Ketchum University, Fullerton, CA, United States – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6906176/
- Department of Medicine, Division of Endocrinology and Institute for Translational Science (ITS), University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston, Galveston, TX – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3649613/
- Cardiology Department, Cairo University, 1 El-Sherifein Street, Abdeen, Cairo 11111, Egypt – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19656312/
- – https://diabetesjournals.org/diabetes/article/56/4/1010/12937/Visceral-Fat-Adipokine-Secretion-Is-Associated
- Department of Clinical Epidemiology, Leiden University Medical Center, 2333 ZA Leiden, The Netherlands – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6832997/
- Department of Nutrition and Dietetics, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Universiti Putra Malaysia (UPM), Serdang, Malaysia – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5507106/
- Division of Epidemiology and Community Health, School of Public Health, University of Minnesota – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3288354/
- Radiology Department, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26755505/
- Institute for Clinical Psychology and Psychotherapy, Technische Universitat Dresden, Dresden, Germany. – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3307043/
- Neuroscience Research Center, Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6633071/
- Division of Population Health , National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion , Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – https://www.cdc.gov/alcohol/fact-sheets/moderate-drinking.htm
- Department of Family Medicine,Hanyang University Medical Centre, Seoul,Republic of Korea – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28641594/
- Healthy Active Living and Obesity Research Group, Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario Research Institute, 401 Smyth Road, Ottawa, ON K1H 8L1 Canada – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4338356/
- Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Baton Rouge, LA – https://journals.lww.com
- Division of Epidemiology and Community Health, School of Public Health, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5315590/
- Department of Prevention of Alimentary Tract Diseases, The Institute of Nursing and Midwifery, Jan Kochanowski University, Kielce, Poland – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6215384/
- Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, Oklahoma, USA – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22284338/
- Department of Food and Nutrition, Kyungsung University, 309, Suyeong-ro, Nam-gu, Busan 608-736, South Korea – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29673541/
- Department of Health and Exercise Sciences, Skidmore College, Saratoga Springs, New York, USA. – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23703835/
- Department of Molecular Endocrinology, Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18332882/
- Oxford Centre for Diabetes, Endocrinology and Metabolism, Churchill Hospital, Oxford, UK – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4845132/
- Department of Health Science, Universidade Estadual de Maringa, Maringa, Parana, Brazil – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24228934/
- University of California, Los Angeles, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, Los Angeles, CA 90095 USA – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5385025/
- Endocrinology Unit, Department of Clinical Medicine and Surgery, ‘Federico II’ University of Naples, Naples, Italy – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31391921/
- Faculty of Nursing and Health Sciences, Notre Dame University-Louaize, Zouk Mosbeh 72, Lebanon – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7333005/
- LECOM Bradenton – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538239/
- Obesity Center CGG, Erasmus MC, University Medical Center Rotterdam, Room D-428, P.O. Box 2040, 3000 CA Rotterdam, The Netherlands – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5958156/
- University of California, Los Angeles, CA 90095, USA – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26356039/
- Multidisciplinary Unit for Biomedical Research, UMIB-FCT, Institute of Biomedical Sciences Abel Salazar (ICBAS), University of Porto, Portugal – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5440253/
- Centro de Farmacologia e Biopatologia Química (U38-FCT), Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade do Porto, Portugal – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3648822/
- Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Rabin Medical Center, Beilinson Hospital, Petach Tikva 49100, Israel – https://parjournal.net/article/view/1860
- Sports Medicine Research Center, Neuroscience Institute, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, IR Iran – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5236497/
- Cosmetic Dermatology, SBC Medical Group, Medical Corporation Shoubikai, Shinjuku-ku Tokyo, Japan – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8627241/
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration – https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/aesthetic-cosmetic-devices/non-invasive-body-contouring-technologies
- Department of Dermatology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27511869/
- Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Pomeranian Medical University in Szczecin, Police, ul. Siedlecka 2, 70-010 Police, Poland – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9459719/
- Klaus Fritz and Carmen Salavastru – https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/jocd.12429