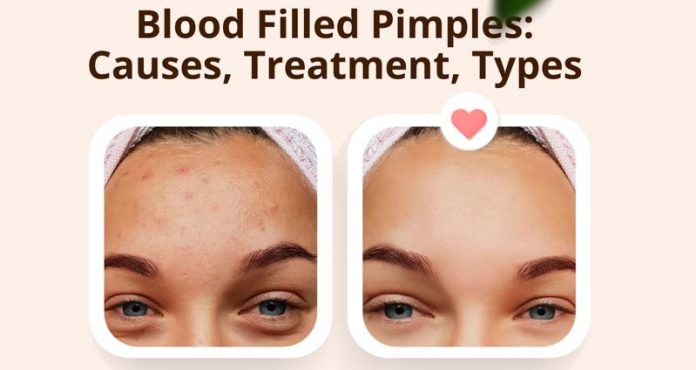
Pimples are one of the most prevalent skin problems that both men and women experience. They commonly arise during puberty. However, they can afflict people of any age. Blood-filled pimples can be a frustrating and embarrassing skin condition, often resulting from acne that has been squeezed or tampered with.
While pimples are common, severe acne can cause long-term scarring and impact self-esteem. Hormonal changes, poor hygiene, and bacterial infections can cause these pimples. Read on to learn about the causes, treatments, and preventive tips associated with blood-filled pimples.
What is a blood-filled pimple?
A blood-filled pimple is acne when a pore becomes clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria. When the pimple is squeezed or tampered with, the blood vessels beneath it may rupture, causing blood to fill the pimple.
Causes of blood-filled pimples
The temptation to pop a pimple can be hard to resist, but it’s essential to understand the potential consequences before giving in. The most common cause of a bloody pimple is popping, scratching, or picking at an existing acne outbreak. When a pimple is popped or scratched, the blood vessels beneath it may rupture, leading to blood filling the pimple. Popping a pimple can push bacteria and oil deeper into the skin, leading to more significant inflammation, increased risk of scarring, and potentially more severe acne outbreaks.
Types of blood-filled pimples
Many types of blood-filled pimples can occur on your face and body:
- Cystic acne: This is a severe form of acne that causes large, painful cysts that can be filled with pus and blood. If you have cystic acne, you may notice several large bumps on your face at once or just one or two huge bumps that take weeks to go away. Cystic acne can be difficult to treat and may result in scarring.
- Hormonal acne: As the name suggests, hormonal acne results from hormonal fluctuations in the body, such as during puberty, menstruation, and pregnancy, producing more oil in the skin pores. Hormonal acne can often result in blood-filled pimples and requires specialized treatment.
- Infected pimples: These infections result when bacteria get into the pores and multiply rapidly, causing redness and swelling around the area on your face where the pimple is located. Infected pimples usually have pus-filled bumps that are painful when touched or squeezed. Infected pimples may also cause scarring if left untreated.
- Folliculitis: Folliculitis occurs when the hair follicles become inflamed due to bacteria, yeast, or other factors. Folliculitis can cause red, itchy bumps that may become filled with blood.
- Abscess: The term abscess is used to describe a pus-filled pocket that occurs when bacteria enter your skin through a crack or wound and infect tissue beneath the skin’s surface. Abscesses are deep, painful infections that can be filled with pus and blood. They usually require medical treatment and can result in scarring if not properly cared for.
It’s important to remember that a mix of circumstances frequently causes these blood-filled pimples, so consult a dermatologist to establish the best course of therapy.
Treatment options for blood-filled pimples
Ideally, please ignore it. Leave the pimple to heal on its own. Avoid disturbing it by picking at it or pressing on it. Use a light cleanser twice a day on the affected area, as this will also help to minimize further outbreaks.
If you continue to suffer from acne that causes blood-filled pimples, prescription medicine may provide relief. Your doctor will assist you in determining what is best for you and may recommend one of the following depending on the severity:
- Topical creams and gels: These are often the first line of treatment for mild to moderate acne. Topical treatments may include benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, and retinoids. These medications can help unclog pores and reduce inflammation.
- Antibiotics: For more severe acne, oral antibiotics may be prescribed to help control the bacteria that cause acne. This can help reduce inflammation and prevent the formation of new pimples.
- Oral medications: In some cases, oral medications such as isotretinoin may be prescribed. These medications work by reducing the size of the oil glands in the skin, which can help prevent the formation of new pimples.
- Drainage and incision: For large or deep pimples, a dermatologist may need to drain the pimple or make a small incision to release the pus and blood. This can help reduce pain and promote healing.
It’s important to note that these treatment options may have potential side effects, and following a dermatologist’s advice and precautions is essential. Additionally, it’s important to avoid squeezing, scratching, or picking at pimples, which can lead to further skin damage and inflammation. Some medications may also have risks for pregnant women or those with certain medical conditions.
Prevention of blood-filled pimples
If you want to keep your skin clear and free of blood-filled pimples, try these tips:
- To begin with, never pick, pop, or squeeze these pimples, as this may increase inflammation and lead to blood-filled pimples and scarring. Additionally, avoid unnecessarily touching your face.
- Establishing a good skincare routine can help prevent acne and blood-filled pimples. This may include gentle cleansing, exfoliating, and using non-comedogenic moisturizers and skincare products.
- Identifying and avoiding triggers that can cause acne outbreaks can be helpful. This may include avoiding greasy or oily products, wearing non-irritating clothing, and avoiding touching or picking at the skin.
- Healthy, balanced diets with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help support healthy skin. Additionally, avoiding sugary and processed foods may help prevent acne outbreaks.
- Acne can be worsened by exposure to the sun, which can cause skin damage. Protecting your skin from the sun is essential with a sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, avoiding peak sun hours, and wearing protective clothing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blood-filled pimples can be a frustrating and painful condition. They can be caused by a variety of factors, such as popping or picking at existing acne, hormonal changes, or infections. Fortunately, several treatment options are available, including topical creams, antibiotics, and oral medications. In some cases, drainage and incision may be necessary to treat more severe cases. Prevention is also crucial, and establishing a good skincare routine, avoiding triggers, and eating a balanced diet can help reduce the risk of blood-filled pimples.
At Kolors Healthcare, we have a team of qualified and experienced dermatologists who can diagnose the underlying cause of your acne and pimples and provide personalized treatment options. By consulting with a qualified and experienced dermatologist, you can get effective solutions for your blood-filled pimples and achieve healthy, clear skin.