When discussing skin issues with your friends, you might have noticed that terms like pimples and acne are often used simultaneously. Did you know both of these terms don’t indicate the same issue? Both acne and pimples are different in appearance and have other causes and types. Read on to learn what pimples and acne are and how they differ.
What Is Acne?
Acne can be defined as a skin issue usually associated with nodules, pimples, cysts, whiteheads, cysts, and blackheads. Acne affects the areas of your skin with highly active oil glands, especially in your face, back, chest, and neck [1].
Acne occurs due to the congestion of hair follicles in the skin layers, accumulation of excess sebum, and dead tissue that can clog the pores in your skin. Acne Vulgaris [2] is commonly found in teenagers and adolescents, while Acne Rosacea is found among grownups [3]. Acne development can be commonly found in various parts of your body, like the chest, back, shoulders, face, arm, and neck.
What are Pimples?
Pimples are defined as a specific symptom of acne, often characterized by pus-filled boils that are reddish in appearance and inflamed. These tiny bumps occur when your hair follicles get infected by bacteria. Open or closed comedones called blackheads or whiteheads are commonly referred to as pimples.
Difference between Acne and Pimples
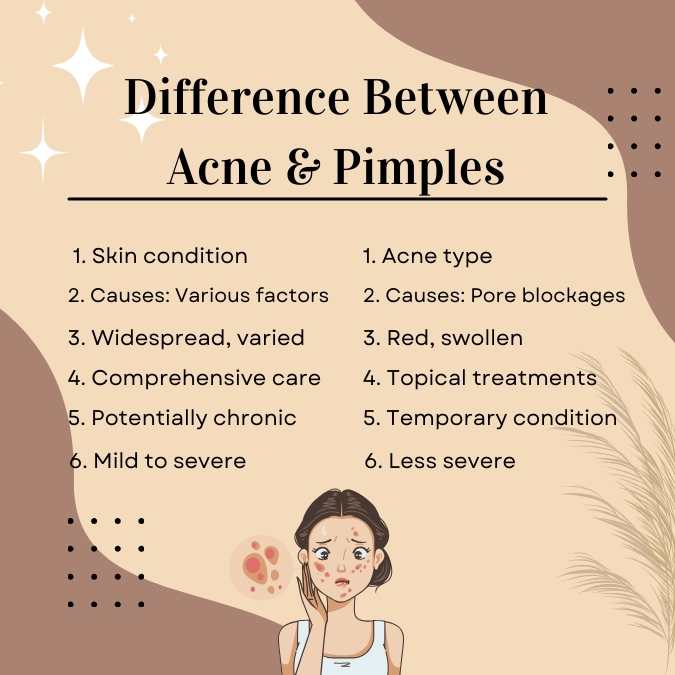
| Feature | Acne | Pimples |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A dermatological condition that affects hair follicles and oil-producing glands. | Manifestation of acne, small, inflamed lesions of the oil glands. |
| Causes | Triggered by hormonal fluctuations, stress, hereditary factors, diet, and certain drugs. | Caused by the clogging of pores with sebum, dead skin cells, or bacteria. |
| Appearance | Occurs in different forms like blackheads, whiteheads, cysts, and deep nodules. | Inflamed, reddish swellings, has a pus-filled centre. |
| Affected Areas | Appears on the face, shoulders, back, and chest. | Face, neck, shoulders, or back. |
| Treatment | Comprehensive skin care regimen and medical intervention might be required in some cases. | Generally treated with over-the-counter solutions. |
| Duration | Lasts for a prolonged period, might become a chronic issue. | Resolves in a few days to weeks, a short-term condition. |
| Severity | Mild to extremely severe conditions. | A milder form of acne. |
Types of Acne
Acne is divided into six types [4], such as:
1. Papules
An elevated bump having a reddish head visible on your skin’s surface is known as a papule. Measuring less than 5 mm in diameter, this acne has no white or yellow centre pus. It also doesn’t have any dark centre like a blackhead.
2. Pustules
With time, this plant will get infected and fill up with yellow or whitish pus on the top, referred to as a pustule. However, not all bumps will change into pustules. It won’t scar your skin. Though it might be tempting to pop acne, avoiding it will help prevent the infection from spreading on your skin.
3. Nodules
This type of acne is characterized by hard lumps, which occur underneath the deep layers of your skin. Nodules can be tender, painful, and inflamed. This type of acne will create dark-looking blemishes and will leave scars on your skin.
4. Cysts
These are huge bumps that are soft to the touch, occurring below the top skin layer. They appear like boils in white or red colour and are filled with pus. This type of acne can be painful and can cause scars.
5. Whiteheads
Closed comedones or whiteheads contain a nucleus with very fine skin covering it. They are firm bumps appearing in flesh colour and don’t have any pus. Whiteheads can make the skin appear wrinkled or very tight.
6. Blackheads
The open comedones or blackheads are prone to oxidation causing blackness, making your skin appear dull. They develop as non-inflammatory and tiny lesions, which occur when the skin pore gets clogged. These pimple lesions usually develop in the epidermis or top layer of your skin and don’t contain dirt filling the pores.
Top 9 Causes of Acne and Pimples
Both acne as well as pimples have similar causes. Specific reasons like accumulation of dead skin cells, too much sebum, and bacteria will clog the sebaceous glands, leading to acne and pimples. Some of the common reasons why you might develop pimples or acne are:
1. Change in Hormones
Any change in hormones in teenagers and adults is a contributing factor to acne and pimple breakouts. Fluctuations in hormone levels cause an increase in sebum production, which will trap dirt and dead cells to clog your skin pores. Adults aged from 20 to 50 years of age will experience hormonal acne caused by bacteria. While people of any gender might face these skin issues, it is likely to be more common among women facing menopause, PCOS or Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome pregnancy or menstrual cycle [5].
Before your menstruation cycle commences, the levels of estrogen and progesterone will go down, which in turn will cause the production of excess sebum [6].
2. Hyperactivity of Sebaceous Glands
Your skin has tiny microscopic glands called sebaceous glands which are responsible for producing sebum [7]. It is a natural oil-like substance that keeps your skin hydrated and prevents it from dryness.
However, sometimes any medical condition or people having oily skin can cause excess sebum secretion, which will trap impurities like dirt, dead cells or debris in your skin, making it perfect for Propionibacterium acnes to thrive and lead to the development of bumps filled with pus [8]. These bacteria will also stimulate an immune response to cause acne breakouts and inflammation.
3. Stress and Anxiety
If your skin is acne-prone, then having a stressful lifestyle can aggravate it further [9]. When you are stressed by a tight work schedule or the loss of a close relative, your body releases stress hormones called androgens and cortisol, which can trigger acne breakouts [10].
The acne induced by stress usually occurs on your chin, nose, and forehead caused by the action of neuropeptides. It might also develop as dilated pores, whiteheads, and blackheads. The skin surrounding the stress acne will appear shiny and look red. Studies reveal that females [11] experience stress acne more than males due to specific effects of stress and anxiety like lack of sleep or disturbed sleep [12].
4. Genetics
Heredity is one of the major contributors to persistent acne [13]. The study by the National Health Service reveals that families with a history of acne will be passing it from one generation to another [14]. If one of your parents has acne-prone skin, your likeliness of developing it is very high. If both your parents experience severe breakouts, then you will develop acne at a young age.
5. Too Much Exfoliation
Using products with harsh chemicals in body care or skin care will strip the natural oils in your skin, hurt it, and cause inflammation, redness, and acne breakouts. Excess use of exfoliation products like scrubs every day will also worsen your acne by causing the spread of bacterial infection [15].
6. Using Comedogenic Products
Some skincare products are comedogenic, indicating they can clog your skin’s pores. Do not use cosmetics or makeup items like oil-based foundations or lanolin or mineral oil as an ingredient if you have acne-prone skin. Residual buildup of makeup products on your skin will also cause dirt and bacterial accumulation, leading to acne, if you leave makeup on your face overnight.
7. Poor Diet
A diet rich in carbohydrates will promote your risk of developing acne. Consuming processed foods with high sugar content will trigger the insulin level, which, in turn, will cause a spike in sebum production. If your diet consists more of animal protein like beef or chicken, then it can trigger acne or pimple breakout [16]. These protein-rich foods have high levels of leucine, an amino acid that causes a hike in inflammation and sebum production. Chocolates also are a huge contributor to acne breakouts, as a 2016 study showed that consuming 99% dark chocolate without any added milk or sugar will worsen acne [17].
While milk chocolate has ingredients like sugar and milk that cause breakouts, the flavonoids in dark chocolate have anti-inflammatory benefits. The cocoa butter in dark chocolate also contains fats like stearic acid and oleic acid, which can clog the skin pores [18].
Choose Best Foods for Pimple-Free Skin
8. High Glycemic Foods
If you love to consume a lot of foods and drinks that contain high glycemic index, it might cause some sudden acne breakouts [19]. Ensure that your diet doesn’t contain sugary beverages like sugary drinks and milkshakes or foods like chips, fries, fast foods, and white bread to prevent acne breakouts.
9. Side Effects of Medications
Studies show that acne is a side effect of using specific drugs like lithium, corticosteroids, anticancer medicines, testosterone, and anabolic steroids [20]. Sometimes, medications that contain bromides or iodides, bodybuilding steroids, or prescription drugs like prednisone might make your acne worse.
Treatment Approaches for Acne and Pimples
There are several treatment approaches available to clear acne and pimples. Consult your dermatologist to get the right type of treatment approach based on the severity of your acne or pimple breakouts.
1. Over The Counter Products
- Benzoyl Peroxide: Choosing an OTC product with Benzoyl Peroxide will help in combating the bacteria responsible for worsening acne breakouts. You may feel irritation as a side effect.
- Retinoids: Choosing products that contain derivatives of Vitamin A, like retinoids, will help in the treatment of whiteheads and blackheads, inflammatory blemishes, pimples, and acne. It can also be useful to treat severe acne conditions like acne vulgaris. Ensure you seek your doctor’s advice before opting for OTC products with retinol, as they can be super drying and irritate the skin.
- Salicylic Acid: Using OTC products like lotions or creams with Salicylic acid, known for exfoliating abilities, will help in controlling the oil production of your sebaceous glands. It also removes dead skin cells to avoid pore blockage, which may cause pimples or acne.
2. Antibiotics
Taking antibiotics orally or applying them topically on the skin will help combat bacteria on the skin surface and lower skin inflammation. Antibiotics will be helpful to tackle severe acne when combined with retinoids or benzoyl peroxide. Antibiotics containing isotretinoin will help shrink the oil glands, reducing sebum production and clogging pores to cut down acne.
3. Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy will be prescribed for women dealing with extreme acne or pimple breakouts due to excess androgen hormones. This treatment option will use a combination of low-dose progesterone and estrogen through contraceptive pills to control acne or pimple breakouts.
4. In-Office Treatment Options
If your acne or pimples don’t respond to antibiotics or OTC products with effective anti-acne ingredients, your doctor will prescribe any treatment options listed below.
- Chemical Peels: This treatment procedure is performed by using a chemical solution to peel the topmost layer to reveal young-looking skin underneath. The chemical solution will contain strong ingredients like phenol or carbolic acid, glycolic acid, lactic acid, trichloroacetic acid, or salicylic acid. Also known as derma peeling, this treatment will focus on removing the topmost layer of your skin to reveal fresh and young skin free from pimples and acne. Your dermatologist will determine the strength of your chemical peel solution from light, medium, and strong based on the severity of your pimple or acne breakouts.
- Microdermabrasion: his procedure is performed by using a specialized device to remove the topmost layer of your skin to sand off the blocked pores. So, the clogged pores on the skin’s surface get eliminated, which can help keep pimples or acne at bay. It is also useful for removing the unsightly deep scars caused by acne and pimples.
- Laser Treatment: Laser treatment is performed by applying pulsating light beams on the skin site with acne or pimples. The laser light beam lowers the sebum production in your skin to reduce the appearance of pimples or acne.
When to Seek Professional Help for Your Acne and Pimple Issues?
Developing skin conditions like acne or pimples is common and might break out at some point in your life. However, it is essential to remember that sometimes it can be worse with inflammation and pain, which is why you must get it treated by a dermatologist [21]. If you see sudden breakouts on your face, chest, back or neck, you must consult your doctor to ensure it is not folliculitis or rosacea. Even though mild cases of pimples or acne can be treated with OTC products, your skin might not respond to them.
In such situations, it is ideal to seek an appointment with your dermatologist to evaluate it and get a prescription for anti-acne treatments and medicines. However, avoid using OTC products when your acne is inflamed or severe; as such, cysts and nodules must be treated only by a dermatologist to prevent risks like scarring. You can schedule an appointment with the dermatologist at Kolors Healthcare to perform a complete evaluation and suggest tests to identify the cause of the trigger and rectify it with treatment.
References
- American Academy of Dermatology Association – https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/acne/really-acne/symptoms
- Dr. Mohamed L Elsaie – https://www.dovepress.com
- American Academy of Dermatology Association – https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/acne/really-acne/adult-acne
- National Institutes of Health, 9000 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, Maryland 20892 – https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/acne
- Office on Women’s Health – https://www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/acne
- Department of Dermatology, Andrology and STDs, Faculty of Medicine, Menoufiya University, Menoufiya, Egypt – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4252966/
- Attila G. Szöllősi, Attila Oláh, Tamás Bíró & Balázs István Tóth (2017) Recent advances in the endocrinology of the sebaceous gland, Dermato-Endocrinology, 9:1 – https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/19381980.2017.1361576
- Department of Molecular and Medical Pharmacology, David Geffen School of Medicine, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, USA. – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23337890/
- American Academy of Dermatology Association – https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/acne/causes/acne-causes
- UPMC HealthBeat – https://share.upmc.com/2018/07/does-stress-cause-acne/
- Brigitte Dreno, Edileia Bagatin, Ulrike Blume-Peytavi, Marco Rocha, Harald Gollnick – https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/ddg.13664
- Neera Nathan, MD, MSHS, Contributor, and Payal Patel, MD – https://www.health.harvard.edu
- Department of Genetics and Computational Biology, QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute, Brisbane, Australia – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8821634/
- NHS England – https://www.nhs.uk
- Amita H. Sutaria; Sadia Masood; Haitham M. Saleh; Joel Schlessinger. – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459173/
- F. William Danby – https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/exd.12180
- Division of Dermatology, Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand – https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26711092/
- Federica Dall’Oglio MD, PhD, Maria Rita Nasca MD, PhD, Federica Fiorentini MD, Giuseppe Micali MD – https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/ijd.15390
- American Academy of Dermatology Association – https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/acne/causes/diet
- Jana Kazandjieva MD PhD, Nikolay Tsankov MD PhD: Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Medical University, Sofia, Bulgaria – https://www.sciencedirect.com
- Cologne, Germany: Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) – https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279211/